贝叶斯分类器实现
1、贝叶斯分类实现(采用python3.6 数据集为arff文件格式)
数据挖掘课老师留的一个实现贝叶斯分类器的练习,数据源为arff格式的文件~下面是使用python语言编写的一个简单的实现案例。
1.1、 arff格式文件介绍
arff文件是Weka默认的储存数据集文件。每个arff文件对应一个二维表格。表格的各行是数据集的各实例,各列是数据集的各个属性。推荐使用
UltraEdit这样的字符编辑软件或者Sublime Text这样的文本编译器查看arff文件的内容。
weather.arff 文件内容如下所示: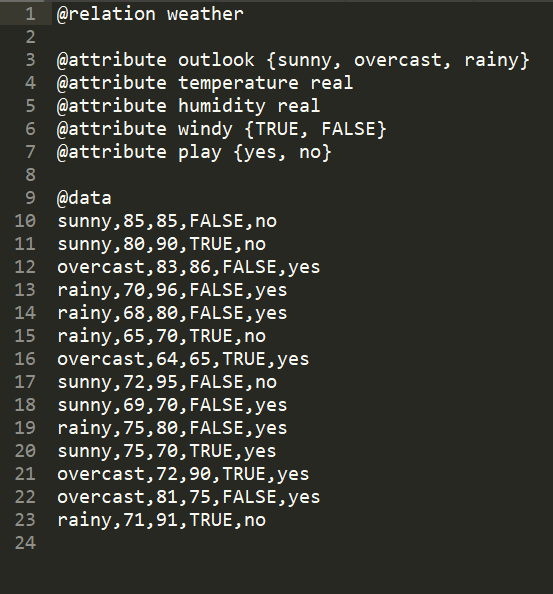
识别ARFF文件的重要依据是分行,因此不能在这种文件里随意的断行。空行(或全是空格的行)将被忽略。
以“%”开始的行是注释,WEKA将忽略这些行。如果你看到的“weather.arff”文件多了或少了些“%”开始的行,是没有影响的。
除去注释后,整个ARFF文件可以分为两个部分。第一部分给出了头信息(Head information),包括了对关系的声明和对属性的声明。第二部分给出了数据信息(Data information),即数据集中给出的数据。从“@data”标记开始,后面的就是数据信息了。
虽然Weka也支持其他一些格式的文件,但是ARFF格式是支持的最好的。因此有必要在数据处理之前把数据集的格式转换成ARFF。
1.2、 arff格式文件读取
1 | import re |
输出结果如下所示:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
['sunny', '80', '90', 'TRUE', 'no']
['overcast', '83', '86', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['rainy', '70', '96', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['rainy', '68', '80', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['rainy', '65', '70', 'TRUE', 'no']
['overcast', '64', '65', 'TRUE', 'yes']
['sunny', '72', '95', 'FALSE', 'no']
['sunny', '69', '70', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['rainy', '75', '80', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['sunny', '75', '70', 'TRUE', 'yes']
['overcast', '72', '90', 'TRUE', 'yes']
['overcast', '81', '75', 'FALSE', 'yes']
['rainy', '71', '91', 'TRUE', 'no']
[['sunny', '85', '85', 'FALSE', 'no'], ['sunny', '80', '90', 'TRUE', 'no'], ['overcast', '83', '86', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['rainy', '70', '96', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['rainy', '68', '80', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['rainy', '65', '70', 'TRUE', 'no'], ['overcast', '64', '65', 'TRUE', 'yes'], ['sunny', '72', '95', 'FALSE', 'no'], ['sunny', '69', '70', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['rainy', '75', '80', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['sunny', '75', '70', 'TRUE', 'yes'], ['overcast', '72', '90', 'TRUE', 'yes'], ['overcast', '81', '75', 'FALSE', 'yes'], ['rainy', '71', '91', 'TRUE', 'no']]
1.3、 实现贝叶斯分类器
1 | import re |